This chapter focuses on the critical evaluation and identification of research methods in order to improve the relevance and innovation of the approaches used in a project. It provides a detailed framework for evaluating existing methods and adapting them to the specific needs of the project, ensuring that research is both robust and state-of-the-art.

Page contents
ToggleIdentification of methods
A literature review A thorough understanding is fundamental to understanding what methodologies have been used in the field, how they have evolved, and their impact. Use the keywords defined earlier in the mindmapping session to find research articles solving this or a similar problem.
Conduct a comprehensive search for academic articles, conference proceedings, and patents to bring together a wide range of methodologies. This research should focus on successful applications and noted failures to provide a balanced view.
Organize the collected methodologies into categories according to their objectives, results and areas of application, which helps identify patterns and trends in methodological development.
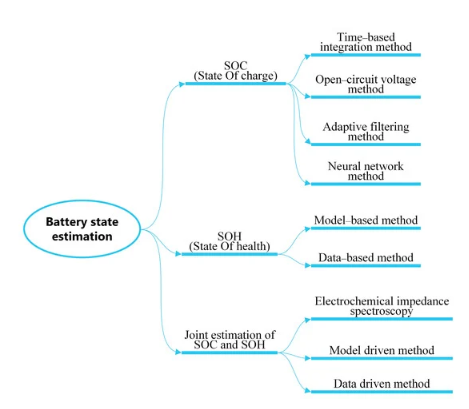
Development of evaluation criteria
Developing robust evaluation criteria is crucial for assessing the suitability of each method :
Efficiency : Measure the success rate of the methodology in achieving its planned results during past implementations.
Efficiency : Evaluate the resources required by the methodology, including time, budget and labor, and its effectiveness in using these resources.
Scalability : Assess whether the methodology can be scaled based on the scope of the project and available resources.
Reproducibility : Consider how easily the method can be replicated in different environments or with different teams.
Ethical considerations : Ensure that methodologies respect ethical standards, particularly in areas involving human or animal subjects.
Comparative analysis
Conducting a comparative analysis allows researchers to objectively evaluate each methodology against the specific needs of the project:
Development of a matrix : Create a matrix to compare each methodology against the evaluation criteria. This visual comparison helps highlight the strengths and weaknesses of each method at a glance.
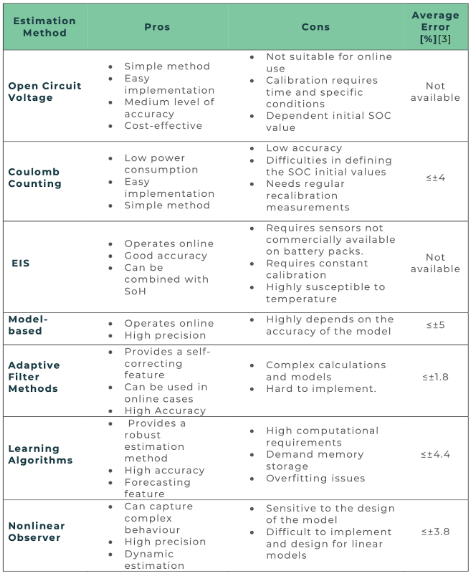
Contextual fit : Discuss the performance of each methodology under the specific conditions of the current project. This includes consideration of environmental, cultural and technological factors that could influence effectiveness.
Adaptation workshops
Adapting and innovating on existing research methodologies is crucial to adapt them to the specific needs of the project and advance the field. These workshops serve as collaborative spaces where researchers can apply modifications to existing methodologies and evaluate their effectiveness in real time:
Scenario-based training : Participants are given specific scenarios that reflect real-world challenges, requiring them to adapt methodologies accordingly. This helps to understand the implications of each change in a controlled environment.
Interdisciplinary groups : Including professionals from diverse disciplines in these workshops encourages the integration of diverse perspectives and techniques, fostering innovative adaptations.
Facilitator orientation : Expert facilitators guide the adaptation process, providing insights into best practices and potential pitfalls. They help ensure that changes are scientifically sound and practically viable.
These sessions encourage the development of entirely new approaches or significant improvements to existing methods:
Brainstorming techniques : Using structured brainstorming techniques such as mind mapping or SCAMPER (Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Repurpose, Eliminate, Reverse) to generate new ideas.
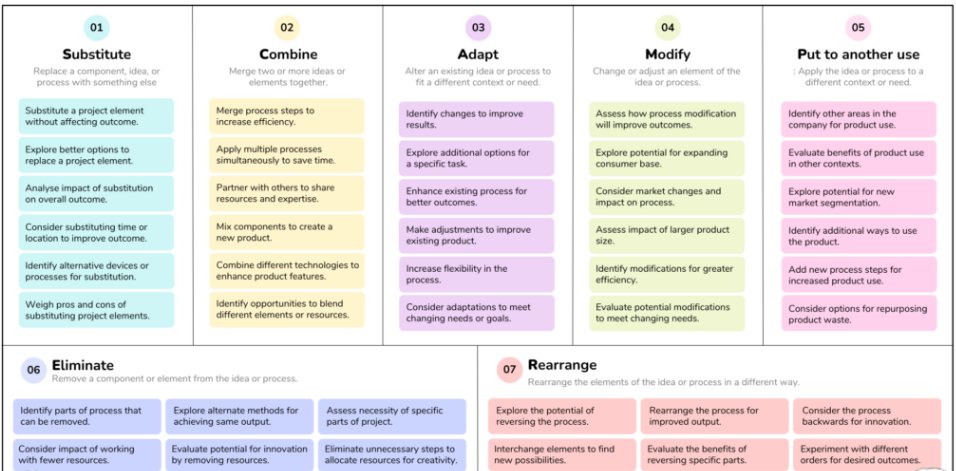

Technological integration : Exploring how new technologies can be integrated into existing methods to improve their efficiency, accuracy or reach. For example, incorporating artificial intelligence and machine learning tools to automate data analysis.
Prototype development : Encouraging the creation of prototypes for new methodologies and testing them in pilot studies to assess their feasibility and effectiveness.
Feedback loops
Establishing effective feedback mechanisms is essential for the continuous improvement of appropriate methodologies; conduct peer reviews of suitable methods to gather critical feedback and suggestions for further refinement. Involve project stakeholders, including non-experts, in reviewing suitable methodologies to ensure that they meet the broader project objectives and are understandable and applicable by all project participants.
By providing hands-on training and facilitating adaptation and innovation of research methodologies, this section equips researchers with the tools and skills necessary to customize methods to their specific project requirements. It ensures that research remains cutting-edge and relevant, capable of addressing the unique challenges and opportunities presented by each new project.