PESTLE analysis is a strategic framework employed in technology monitoring to assess external macro-environmental influences that may affect a specific technology or the entire technology landscape. It focuses on six main aspects: Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal and Environmental factors. This method helps organizations understand the broad contextual influences that shape the technology environment.

Page contents
TogglePESTLE analysis in the strategic framework
To perform a PESTLE analysis in technology monitoring, it is essential to examine government policies, regulations, and political stability that may influence technology. It is also crucial to consider how political decisions and geopolitical events could affect the development and adoption of technology. Next, assessing economic conditions such as inflation, exchange rates, and economic stability helps understand how these factors may influence the financing of technology initiatives, market demand, and overall financial health.
Societal trends, cultural attitudes, demographics, and consumer behaviors are analyzed to determine how these social factors might influence the acceptance, adoption, or rejection of technology by different populations. Furthermore, assessing the current state of technology, innovation trends, and the pace of technological change is necessary to understand how advancements, including competing technologies, may impact the success of the targeted technology. .
The analysis should also include a review of legal and regulatory considerations, including compliance with industry standards, intellectual property laws, data protection regulations, and other legal frameworks that may affect development and deployment. of technology. Finally, environmental sustainability, climate change, and ecological factors should be considered to evaluate how the technology aligns with environmental regulations and how changing attitudes toward the environment might influence its acceptance.
The benefits of PESTLE analysis include a comprehensive environmental assessment that provides an overview of the macro environment and helps organizations formulate strategic plans that are not only based on internal factors but also take into account external forces that shape the technological landscape. This analysis is also beneficial for the proactive management of risks associated with technological developments and improves the adaptability of organizations in the face of changes in the external environment that may impact the technology.
However, PESTLE analysis can be complex due to the comprehensive nature of the factors to be examined, requiring careful consideration and prioritization. Additionally, the strong interconnection between the factors analyzed can make it difficult to isolate the impact of a single factor, sometimes making it difficult to understand the specific dynamics that influence the technology.
PESTLE analysis of a company
This analysis will explore the macro-environmental factors that influence EcoTech's operations and strategic decision-making in the renewable energy sector.
Political Factors:
- Government support: EcoTech benefits from government incentives for renewable energy companies, including tax reductions and subsidies for research and development, strengthening its financial position and market entry strategies.
- International trade policies: Trade agreements and tariffs affect EcoTech's supply chain and pricing, especially in markets where the company imports components or exports its technologies.
- Regulatory environment: Continuing changes in environmental regulations require EcoTech to adapt its technologies to comply with stricter standards, impacting both product design and market strategy.
Economic Factors:
- Economic fluctuations: Global economic volatility can affect investments in green technologies. During times of economic recession, capital-intensive industries like renewable energy may face budget cuts.
- Market demand: There is a growing economic demand for sustainable and renewable energy sources, driven by consumer preference and industrial adaptation to cleaner energy standards.
- Cost of materials: Prices of raw materials needed to produce solar panels and other renewable technologies may fluctuate, impacting EcoTech's cost structure and pricing strategies.
Social Factors:
- Public awareness and preferences: Increasing awareness of climate change issues and a shift towards eco-friendly products are driving demand for EcoTech offerings.
- Demographic changes: Urbanization and increasing energy consumption in developing regions can open new markets for EcoTech products.
- Social movements: Movements towards sustainability and reducing carbon footprints can positively influence the EcoTech market by increasing consumer and business demand for green technologies.
Technological Factors:
- Innovation rate: Rapid advances in renewable energy technologies, such as improved solar panel efficiency and energy storage solutions, require EcoTech to continually innovate to remain competitive.
- Digital transformation: The integration of IoT and smart technologies into renewable energy solutions presents opportunities for product improvements and new services.
- Competition from alternative technologies: The development of new, potentially more cost-effective renewable technologies by competitors may threaten EcoTech's market share.
Legal Factors:
- Intellectual property : EcoTech must protect its innovations with patents and copyrights to maintain its competitive advantage and prevent imitation.
- Compliance requirements: EcoTech must comply with various national and international environmental laws and regulations, which can be complex and costly but essential to the operation.
- Health and safety standards: As a technology company, EcoTech must adhere to strict health and safety regulations to ensure safe operations and avoid liability.
Environmental factors :
- Impact of climate change: As a renewable energy company, EcoTech's products are favorably viewed in climate change mitigation strategies. This alignment with global efforts to combat climate change improves its brand image and marketability.
- Resource scarcity: The scarcity of certain raw materials needed for renewable technologies can lead to increased costs and supply chain challenges, requiring strategic planning and alternative sourcing strategies.
- Ecological innovations: There is an opportunity for EcoTech to take the lead in developing and implementing technologies with minimal environmental impact, thereby consolidating its position in the market as an environmentally responsible company.
PESTLE analysis for technological monitoring
Let's create a PESTLE analysis for a hypothetical photovoltaic panel technology, which we'll call SolarTech. The ideas given for a business are perfectly legitimate for a technology.
Political Factors:
- Government support: SolarTech benefits from favorable government policies, such as grants and tax credits for green technologies, making it easier to invest in and adopt solar solutions.
- Regulatory standards: Regulations regarding the installation and use of solar panels can vary greatly from region to region, influencing SolarTech's market strategy.
- International agreements: Climate and renewable energy agreements may open new markets or impose restrictions that affect the export of SolarTech technologies.
Economic Factors:
- Economic trends: Global economic fluctuations can influence capital expenditures for renewable energy infrastructure, directly affecting demand for SolarTech panels.
- Cost of raw materials: Volatility in prices of silicon and other necessary materials may affect production costs and therefore SolarTech's price competitiveness.
- Financial incentives: Incentives such as financing facilities for consumers and businesses could increase demand for solar panels.
Social Factors:
- Environmental awareness: Growing awareness of environmental issues is driving the adoption of renewable energy solutions, benefiting SolarTech.
- Technology Adoption: The growing acceptance of renewable technologies by the general public and industries could open up vast new markets for SolarTech.
- Demographic changes: Increasing urbanization and densification of cities may increase demand for building-integrated renewable energy solutions.
Technological Factors:
- Innovations: Continuing advancements in photovoltaic technology, such as improving the efficiency of solar cells, provide opportunities for SolarTech to differentiate itself from competitors.
- Compatibility with other technologies: Integration with energy storage technologies and intelligent energy management systems can improve the appeal of SolarTech's products.
- Obsolescence: The speed of technological progress can also make current products obsolete more quickly, posing a risk to long-term investments.
Legal Factors:
- Intellectual property : Protecting innovations through patents is crucial to maintaining SolarTech's competitive advantage against imitations and competing products.
- Regulatory conformity : Compliance with international and national safety and environmental regulations is essential to SolarTech's operation.
- Disputes: Risks of litigation related to intellectual property or the environmental impacts of products may require significant legal and financial attention.
Environmental factors :
- Sustainability : SolarTech can benefit from its commitment to sustainability, an increasingly important factor for consumers and business partners.
- Climate impact: Extreme weather conditions influenced by climate change can affect the performance of solar installations and influence product design.
- Environmental regulations: Strict laws on emissions and decarbonization can increase demand for photovoltaic panels, but also impose compliance challenges.
Tools for a PESTLE analysis
Like the SWOT analysis, there is a generic PESTLE matrix.

Simply fill in the areas that interest us.

Under PESTLE analysis, there is no specific tool like WOTS matrix used for SWOT analysis. However, several methods can be used to structure and visualize the results of a PESTLE analysis, thus making the process clearer and facilitating strategic decision-making.
Causality diagrams can be used to explore and visualize the relationships between different PESTLE factors and their potential impact on the organization. This helps identify causal chains and understand how different elements of the external environment interact with each other and affect the business.
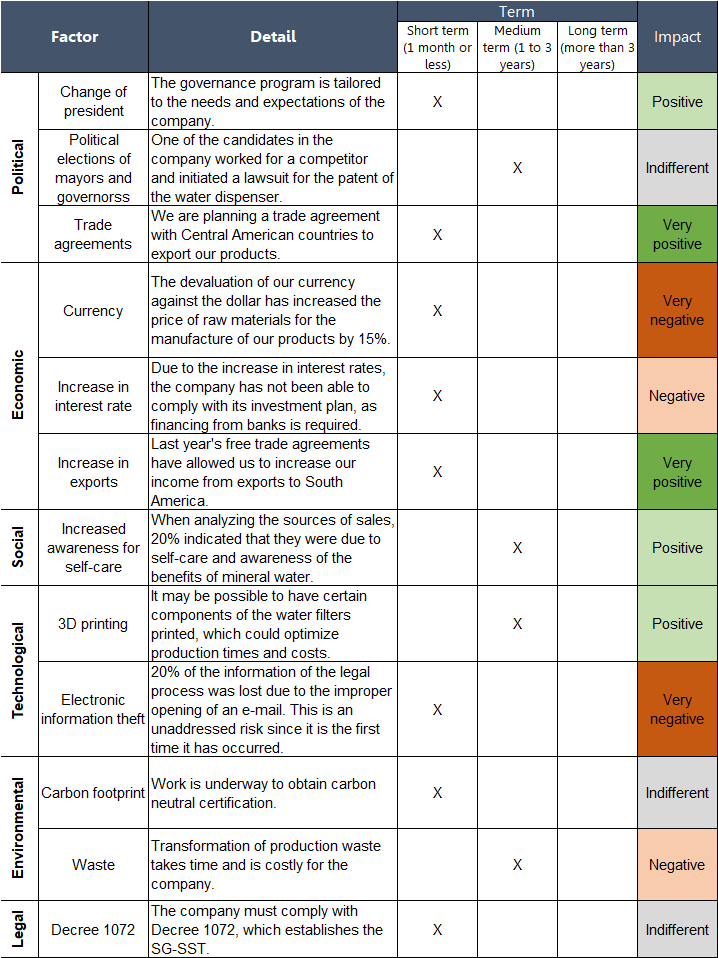
Pros and Cons of PESTLE Analysis
Here is a comparative table of the advantages and disadvantages of SWOT analysis compared to other strategic frameworks such as PESTLE analysis, Porter's Five Forces, Ansoff Matrix, BCG Matrix, and Scorecard Prospective. This table illustrates how SWOT analysis stacks up to these methods in terms of versatility, focus, and usefulness in strategic planning.
| Strategic Framework | Benefits | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| SWOT analysis | – Simple and easy to use.- Offers a balanced view of internal and external factors.- Flexible, can be used with other strategic tools.- Good for brainstorming. | – Lack of depth in competitive analysis. – May be too simplistic, lacking complex dynamics. Don't prioritize factors. |
| PESTEL analysis | – Focuses on external macro-environmental factors that could affect the organization. – Helps understand market growth or decline. | – Does not consider internal factors. – May be too broad, lacking focus on specific strategies. |
| Porter's Five Forces | – Provides in-depth analysis of industry structure and competitive intensity. – Helps understand the profitability of industries. | – Mainly focuses on industry level analysis, not individual companies. – Can be complex and time consuming to analyze. |
| Ansoff matrix | – Focuses on growth opportunities. – Clear options for market and product development strategies. | – Does not consider potential obstacles or threats. – Mainly suited for growth strategies, less for contraction or stability. |
| BCG matrix | – Helps allocate resources based on product performance and market growth. – Useful for large companies with diversified product portfolios. | – Can oversimplify complex market dynamics. – Less effective in fast-paced industries where product life cycles are short. |
| Prospective Dashboard | – Links strategic objectives to performance indicators.- Considers financial and non-financial aspects.- Promotes strategic communication within the organization. | – Implementation can be complex and resource intensive. – Requires ongoing updates and may require significant cultural changes in the organization to be effective. |