Scenario planning in technology intelligence involves creating and analyzing different hypothetical scenarios to anticipate possible future developments in the technology landscape. It is a strategic forecasting tool that helps organizations prepare for a range of possible futures, allowing them to make more informed decisions in the present.

Page contents
ToggleHow to conduct scenario planning
Identification of key uncertainties: Identify critical uncertainties that could significantly impact the technology landscape. These uncertainties may be technological breakthroughs, regulatory changes, market dynamics or other factors presenting a high level of uncertainty.
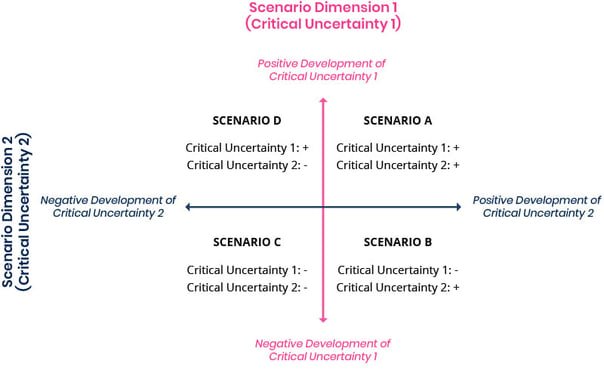
Scenario development: Create multiple scenarios based on different combinations of uncertainties. Each scenario should present a plausible and internally coherent narrative for how these uncertainties might play out. Scenarios should cover a range of possibilities, from optimistic to pessimistic.
Impact assessment: Evaluate the potential impacts of each scenario on the organization and technology by question. Consider how each scenario could affect market conditions, competitive dynamics, regulatory environments and overall business strategy.
Strategic responses: Develop strategic responses for each scenario. These responses should describe how the organization might adapt, innovate, or pivot in response to the conditions described in each scenario. This helps prepare for a range of potential futures.
Signal monitoring: Continually monitor signals and indicators that might suggest which scenario is unfolding. Regularly update scenarios based on new information and adjust strategic responses accordingly.
Pros and Cons of Scenario Planning
Anticipation of change: Scenario planning allows organizations to anticipate and prepare for a range of potential changes, making them more resilient in the face of uncertainty.
Strategic flexibility: By developing strategic responses for multiple scenarios, organizations strengthen their strategic flexibility, allowing them to quickly adapt to changing circumstances.
Improved decision making: Scenario planning provides decision makers with an in-depth understanding of the potential future landscape, improving the quality of decision-making in the present.
Risk mitigation: Organizations can proactively identify and mitigate risks associated with various scenarios, reducing the impact of unexpected developments on technology.
Resource intensity: Scenario planning can be resource intensive, requiring significant time and effort to identify uncertainties, develop scenarios, and evaluate their impacts.
Uncertainty and complexity: The future is inherently uncertain, and the complexity of scenarios can make it difficult to predict which one will actually come true. Organizations must be prepared for ambiguity.
Example of scenario planning on technology monitoring
Here is an example of a scenario planning analysis comparing two technologies:
Scenario 1: Market disruption by emerging technology:
- Description : A new disruptive technology is emerging in the market, offering superior functionality compared to existing solutions.
- Impact on Technology A:
- Technology A could face increased competition and erosion of market share as customers shift to the new technology.
- The company may need to invest in research and development to innovate and differentiate its product offerings.
- Impact on Technology B:
- Technology B may experience a decline in demand as customers migrate to the new technology.
- The company may need to explore strategic partnerships or acquisitions to remain competitive in the market.
Scenario 2: Regulatory changes affecting data privacy:
- Description : Strict regulatory changes are being introduced, imposing tougher requirements on privacy and data protection.
- Impact on Technology A:
- Technology A, with its strong focus on data privacy and compliance, could benefit from the new regulations, gaining a competitive advantage over less compliant competitors.
- The company may need to allocate resources to ensure continued compliance and educate customers on the importance of data security.
- Impact on Technology B:
- Technology B may face challenges adapting to new regulatory requirements, potentially resulting in fines or legal issues for non-compliance.
- The company may need to invest in updating its technology infrastructure and processes to meet new standards.
By considering multiple scenarios through scenario planning, stakeholders can gain insights into potential future developments and prepare proactive strategies to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities. This analysis helps inform decision-making and guide actions to navigate uncertainty and achieve long-term success in the market.
Tools for scenario planning
In order to define the scenarios, it is necessary to take into account the PESTLE analysis and the risk matrix worked previously.
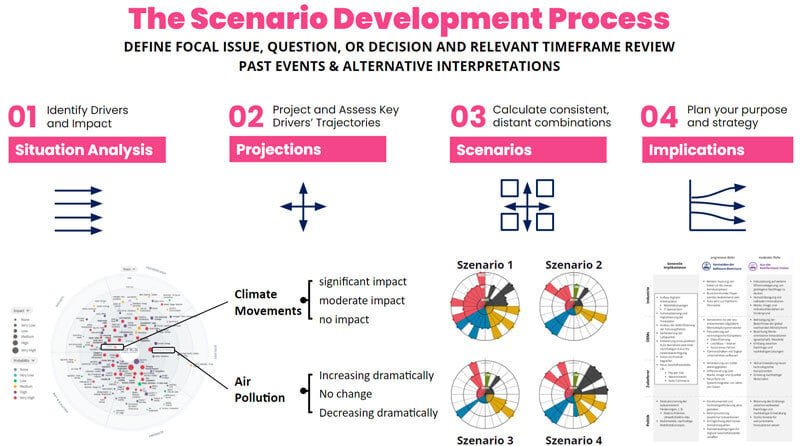
Once an organization has explored and selected the key factors influencing its environment, it must identify critical uncertainties and extrapolate the different plausible possibilities that could arise for each factor. The time horizon to consider is between five and ten years (compared to the two to five year outlook offered by emerging trends and technologies).
Scenario planners must project the trajectory each factor might follow, typically ranging from one extreme to the other, for example, no impact to significant impact, dramatic decrease to dramatic increase, system collapse to transformation. system, etc.
As a reminder, this was achieved in risk management.
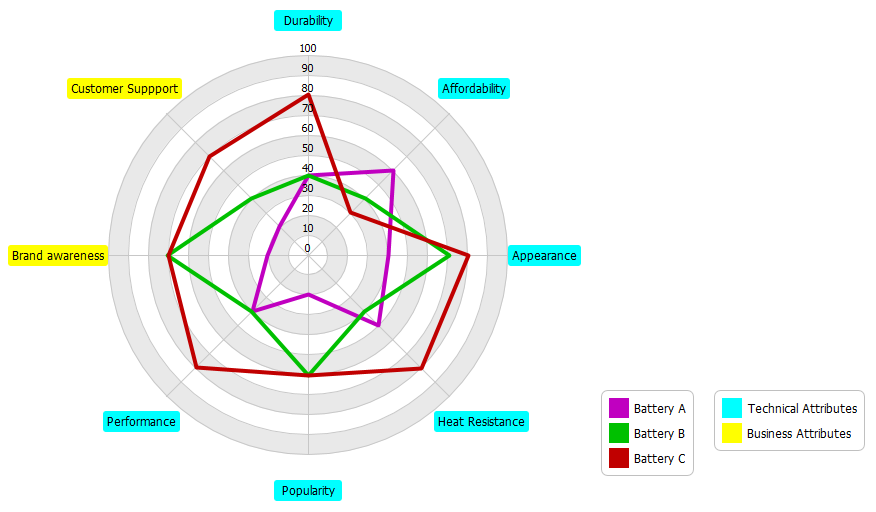
It is possible to qualify and quantify all the scenarios with KPIs, this makes it possible to create a spider web diagram (or radar, polar, Kiviat, it's the same thing) in order to understand the different impacts of the proposed scenarios.
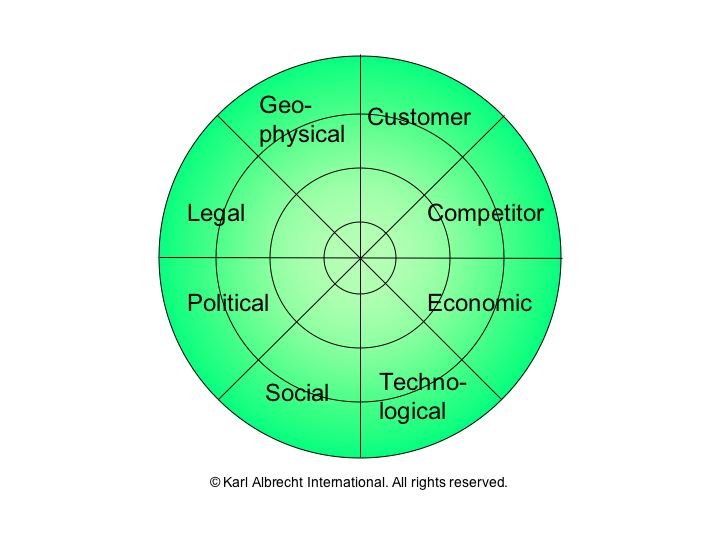
Remember to use PESTLE categories.
There are many methods to define the implications of scenarios like change rating where the tracing possible futures where the potential futures, but we won't go into the design details of these three graphics.
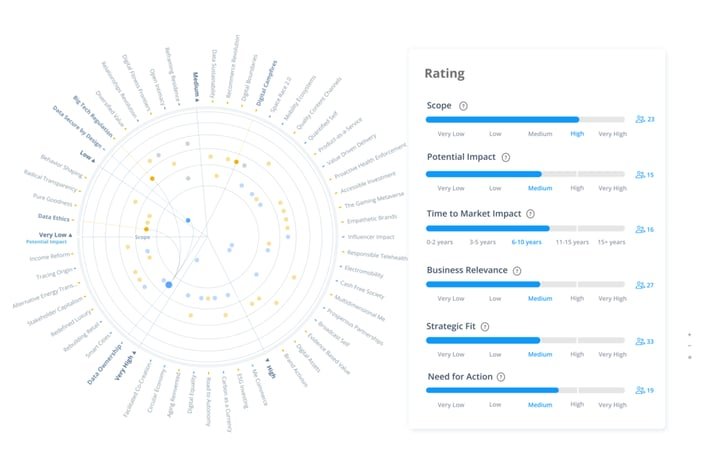
Visualize their level of impact, likelihood and reach, then identify which ones are most critical and influential for your future. Fine-tune yourself to focus on the drivers of change that will give you the most valuable insights into the future.
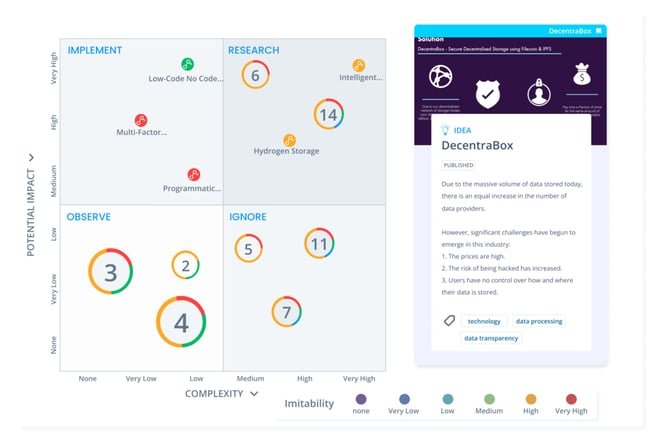
Determine the criticality of each scenario based on its potential impact. Use the Matrix view to visualize priority level and highlight strategic focus areas for the business. Focus on the scenarios most critical to future success.
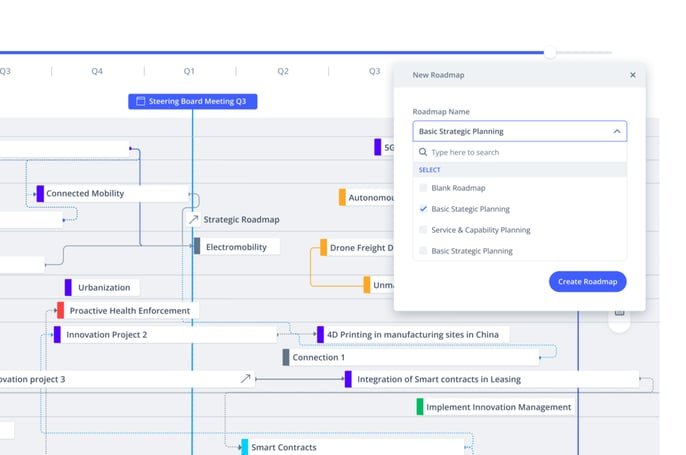
Use the roadmap to visualize potential futures by indicating key events within clear and realistic timelines. Use these pathways to identify related actions to take to achieve the result most desirable. You could call this “Agile Backcasting” to identify the right time to act.